Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is an advanced imaging technology that visualizes the internal structures and soft tissues of the body.
It uses a strong magnetic field and radio waves to produce highly detailed images of the body, which are reconstructed by a computer. MRI is a very safe imaging technique with no radiation exposure.
Brain/Head
MRI is excellent for assessing the brain and spinal canal. It is used to detect brain abnormalities, tumours, strokes and neurological diseases such as multiple sclerosis. It can also identify disorders of the pituitary gland, vision pathway and inner ear.
Spine
MRI is most commonly used to detect bulging, degenerated or herniated intervertebral discs. For patients who have had lower back surgery, MR with contrast is the best tool to distinguish recurrent disc problems versus scarring.
Joints
For joints (ankles, elbows, knees, hips, shoulders, wrists), MRI provides detailed assessment of soft tissues and anatomical structures. Abnormalities and injuries of the ligaments, tendons, cartilage and bones can be accurately detected.
Abdomen
MR with contrast rivals CT in assessment of solid organs such as kidneys, liver, spleen, pancreas, and reproductive organs. It can detect or rule out cancerous tumours and characterize and stage diagnosed tumours, determining the size, extent and spread.
Angiography
MR angiography is a non-invasive way to assess blood vessels. It can diagnose and characterize cerebral aneurysms, investigate peripheral atherosclerosis (e.g. poor circulation in extremities) and evaluate strokes.
CT Scan
A CT (computerised tomography) scanner is a special kind of X-ray machine. Instead of sending out a single X-ray through your body as with ordinary X-rays, several beams are sent simultaneously from different angles.
CT scans are far more detailed than ordinary X-rays. The information from the two-dimensional computer images can be reconstructed to produce three-dimensional images by some modern CT scanners. They can be used to produce virtual images that show what a surgeon would see during an operation.
CT scans have already allowed doctors to inspect the inside of the body without having to operate or perform unpleasant examinations. CT scanning has also proven invaluable in pinpointing tumours and planning treatment with radiotherapy.
X-ray
An X-ray machine produces a small burst of radiation that passes through the body, recording an image on photographic film or a special digital image recording plate.
A simple X-ray image can be extremely informative. For example it can show whether or not a bone is broken or whether or not there is a shadow on the lung.
Special X-ray techniques can also be used to investigate other problems with the soft tissues of the body. By injecting special dye into arteries and/or veins the blood vessels can be made visible.
USG
An ultrasound scan, sometimes called a sonogram, is a procedure that uses high frequency sound waves to create an image of part of the inside of the body, such as the heart.
Sonography is a non invasive imaging modality using sound waves and is extremely safe even in pregnancy as it does not involve any radiation.
Sonography has applications for the entire body from head to toe. Male or female from infant to adult, throughout your lifetime, sonography can play an important role in your healthcare.
2D Echo
Echocardiography can provide excellent images of the heart, paracardiac structures, and the great vessels. The purpose of this study is to determine the size of your heart, to evaluate how well your heart is functioning or pumping and to assess the structure and function of the valves within the heart. A 2-D (or two-dimensional) echocardiogram is capable of displaying a cross-sectional ``slice`` of the beating heart, including the chambers, valves and the major blood vessels that exit from the left and right ventricle.
During a standard echo, the sound waves are directed to the heart from a small hand-held device called a transducer, which sends and receives signals. Heart walls and valves reflect part of the sound waves back to the transducer to produce pictures of the heart. These images appear in black and white and in color on a TV screen. They're selectively recorded, and later reviewed and interpreted by a cardiologist (heart specialist).
From the pictures it is possible to measure the size of each part of your heart, to study motion and appearance of the valves and the function of the heart muscle. Your physician uses the measurements to determine how your heart is working and whether or not any abnormalities are present.
A Doppler echo is often done at the same time in order to determine how the blood flows in your heart. The swishing sounds you hear during the test indicate blood flowing through the valves and chambers.
Stress Test / TMT
Stress testing provides information about how your heart works during physical stress. Some heart problems are easier to diagnose when your heart is working hard and beating fast. It is also called as exercise ECG testing, treadmill testing, exercise stress test.
Cardiovascular exercise stress testing in conjunction with an ECG has been established as one of the focal points in the diagnosis and prognosis of cardiovascular disease, specifically coronary artery disease (CAD).
PFT / Spirometry
Spirometry is a kind of Lung / pulmonary function test that measures airflow.
By measuring how much air you exhale, and how quickly, spirometry can evaluate a broad range of lung diseases.
In a spirometry test, while you are sitting, you breathe into a mouthpiece that is connected to an instrument called a spirometer. The spirometer records the amount and the rate of air that you breathe in and out over a period of time.
ECG
The electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a diagnostic tool that is routinely used to assess the electrical and muscular functions of the heart.
An ECG is done to measure:
- Any damage to the heart
- How fast your heart is beating and whether it is beating normally
- The effects of drugs or devices used to control the heart (such as a pacemaker)
- The size and position of your heart chambers
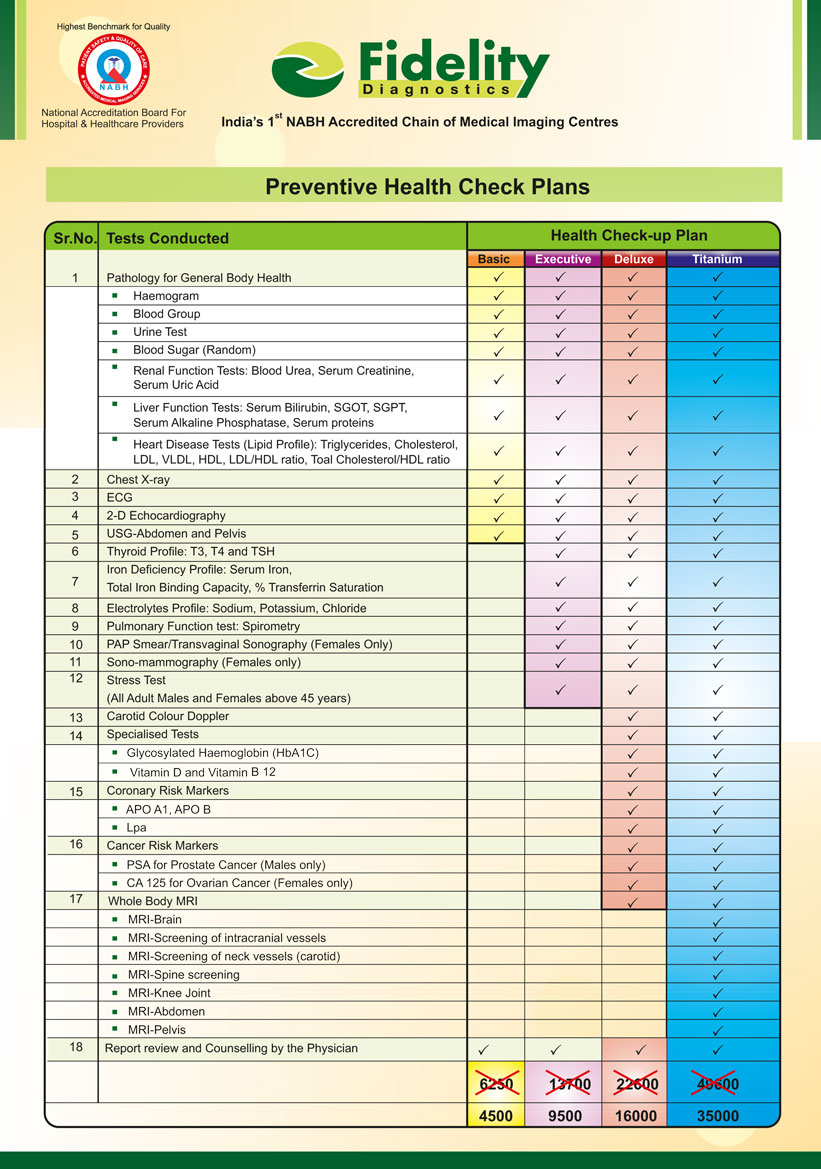
Prevention is better than cure! Regular health checkups are a valuable tool in maintaining good health. Health checkups aim at detecting illness at an early stage or better still prevent illness occurring in the first place. With changes in life style, diseases like diabetes, hypertension, obesity, and heart diseases etc. are affecting the urban Indian population. Most of these diseases are “silent”. We often do not have any early symptoms and regular screening tests are therefore the only way to early detection.
Fortunately, these diseases can be easily prevented or managed, if detected early. Regular health checkups coupled with life style changes can go a long way in the prevention, early detection and cure (good control) of these diseases.
Fidelity Diagnostics offers standardized preventive health check packages designed to preserve and promote good health. Degrading ecological conditions coupled with ever stressful economic situations has today taken their toll on our health. With growing health risks, it is essential that we take preventive measures in order to avoid major health complications.
Fidelity Diagnostics offers a range of crucial health checkups for men and women in every age group. The significant objectives of these checkups are to identify apparent and latent health problem with the use of highly advanced medical technologies and state of the art equipment. All the diagnostic packages are planned and designed by medical professionals with years of experience behind them.