Fidelity Diagnostics offers a number of screening exams that can help identify certain diseases in their earliest stages — where they have the highest probability of successful treatment.
Why Preventive Screening?
Screening exams are designed to look for diseases before they cause symptoms. Early detection of diseases such as coronary artery disease and colon cancer before they cause symptoms can help you and your doctor slow or halt disease progression.
A screening exam might be right for you if you are over 50 years of age (men over age 40 are candidates for a heart scan) and have no symptoms of disease but are concerned about your health due to risk factors such as age, family history, diabetes, smoking or high cholesterol.
Every patient is unique and screening scans aren’t for everyone. We encourage you to talk to your doctor about your risk factors and which screening exams might be right for you. If you have symptoms which you specifically want investigated, please speak to your doctor about a diagnostic scan.
Screening Exams
Why Is MRI Whole Spine Screening Done?
- Find problems of the spinal discs, such as a ruptured disc. The test may also show if a disc is pressing on a nerve
- Find areas of the spine where the canal is abnormally narrowed
- Find tumors affecting the bones or nerves of the spine. The tumors that most commonly spread to the spine include those from prostate, breast, or lung cancer.
- Find compression fractures of the spine.
- Check areas of joint inflammation or bone loss
- Find areas of the spine that do not have good blood supply.
- Find an infection.
- Find nerve damage caused by injury or disease
- Check problems of the spine that have been present since birth (congenital).
Why Is MRI Brain Screening Done?
A brain MRI can be used to diagnose and monitor many diseases and disorders that affect the brain, including:
- Birth defect
- Bleeding (subarachnoid bleed or bleeding in the brain tissue itself)
- Family history of aneurysms
- Infection, such as brain abscess
- Tumors (cancerous and noncancerous)
- Hormonal disorders (such as acromegaly, galactorrhea, and Cushing syndrome)
- Multiple sclerosis
- Stroke
An MRI scan of the head can also determine the cause of:
- Muscle weakness or numbness and tingling
- Changes in thinking or behavior
- Hearing loss
- Headaches when certain other symptoms or signs are present
- Speaking difficulties
- Vision problems
- Dementia
Why is Sonomammography done?
- When a breast lump (mass) or a general lumpiness is felt in the breast
- To determine if the abnormality detected through mammography or a palpable lump is a fluid-filled cyst or a solid tumour
- Breast tissue is too dense to be assessed accurately by mammography
- In high risk patients with family history of breast cancer, past history of breast cancer or in females older than 35 years of age as a preventive measure to screen for breast cancer
- Additional method to evaluate the breast, when mammography is not so clear
Sonomammography or breast ultrasound is a non-invasive procedure performed to assess the breasts and the blood flow to areas inside it. This test allows quick visualization of the breast tissue.
A breast ultrasound or sonomammography is recommended for women,

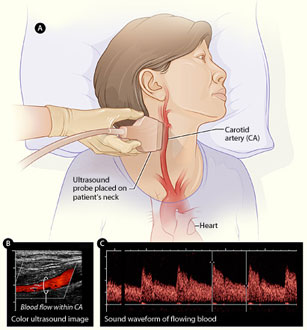
Why is Carotid Doppler done?
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- High cholesterol
- Family history of stroke or heart disease
- Recent transient ischemic attack (TIA) or stroke
- Abnormal sound in carotid arteries (bruit), detected by your doctor using a stethoscope
- Coronary artery disease
Your doctor will recommend carotid ultrasound if you have transient ischemic attacks (TIAs) or certain types of stroke and may recommend a carotid ultrasound if you have medical conditions that increase the risk of stroke, including:
Why is Spirometry / PFT done?
Spirometry is a common test used to assess how well your lungs work by measuring how much air you inhale, how much you exhale and how quickly you exhale. Spirometry is used to diagnose:
- Asthma
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Effect of smoking on lungs
- Other conditions that affect breathing.

